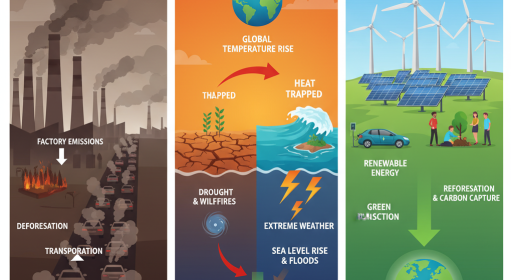
Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances or products into the environment, poses significant threats to ecosystems, human health, and economies worldwide. Its pervasive nature affects air, water, soil, and even extends to noise and light, leading to complex global challenges.
Types of Pollution and Their Causes
- Air Pollution: Emissions from industrial activities, vehicular exhaust, and the burning of fossil fuels release pollutants like particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. Natural events such as wildfires and volcanic eruptions also contribute.
- Water Pollution: Discharge of industrial waste, agricultural runoff laden with pesticides and fertilizers, and untreated sewage introduce contaminants into water bodies. Oil spills and plastic waste further degrade aquatic environments.
- Soil Pollution: Deposition of hazardous chemicals, heavy metals, and improper disposal of industrial waste lead to soil contamination. Excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture also depletes soil quality.
Global Impacts of Pollution
- Human Health: Air pollution is a leading environmental risk, causing approximately 7 million premature deaths annually due to diseases such as stroke, heart disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, and respiratory infections.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Water pollution contributes to waterborne diseases, while soil contamination can lead to the accumulation of toxins in the food chain.
- Environmental Degradation: Pollution disrupts ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and habitat destruction. For instance, plastic pollution in oceans harms marine life, and acid rain from air pollutants damages forests and aquatic habitats.
- Economic Consequences: The economic burden of pollution is substantial, encompassing healthcare costs, reduced labor productivity, and environmental remediation expenses. For example, air pollution alone accounts for more than 1 in 8 deaths globally, underscoring its significant economic impact.
- Climate Change: Certain pollutants, such as black carbon and methane, are potent climate forcers, contributing to global warming. Additionally, deforestation and land degradation release stored carbon, exacerbating climate change.
Mitigation Strategies
- Policy and Regulation: Implementing and enforcing environmental regulations to limit emissions and discharges is crucial. International agreements, such as the anticipated Global Plastic Treaty, aim to address pollution on a global scale.
- Technological Innovations: Advancements in cleaner production technologies, renewable energy sources, and waste management can significantly reduce pollution levels.
- Public Awareness and Education: Informing communities about pollution sources and impacts encourages sustainable practices and consumer choices.
- Sustainable Practices: Adopting sustainable agricultural methods, promoting public transportation, and reducing single-use plastics contribute to pollution reduction.
Addressing pollution requires a concerted global effort, integrating policy measures, technological advancements, and individual actions to safeguard environmental and public