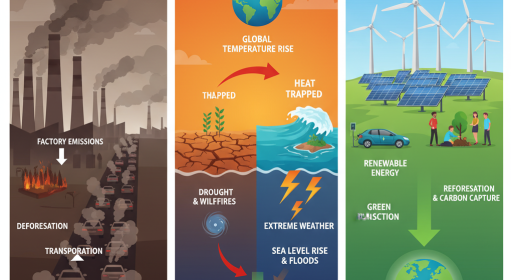
Reducing Emissions (Mitigation)
Clean Energy Transition
- Solar Power: Convert sunlight to electricity via photovoltaic panels
- Wind Energy: Turbines generate power from wind (onshore/offshore)
- Hydropower: Dams use flowing water to produce electricity
- Geothermal: Iceland runs on 100% renewables using underground heat
Energy Efficiency Upgrades
- Switch to LED bulbs (use 75% less energy)
- Improve home/school insulation
- Use smart power strips to prevent phantom loads
Sustainable Transportation
- Bike/walk infrastructure improvements
- Advocate for better public transit
- Support electric vehicle charging stations
Preparing for Impacts (Adaptation)
Climate-Resilient Infrastructure
- Green roofs to manage stormwater
- Flood barriers in vulnerable areas
- Urban tree canopies to reduce heat islands
Sustainable Land Use
- Plant native trees to restore habitats
- Develop drought-resistant crops
- Implement circular economy principles to reduce waste
Ecosystem Protection
- Support marine conservation (Oceana, WWF)
- Reduce plastic pollution harming ocean life
📹 Watch Our Planet (Netflix) to understand fragile ecosystems
Success Stories
- Costa Rica: Runs on 99% renewable energy
- Netherlands: Flood-resistant urban design
- California: School districts going solar
📺 Watch This: DW: How Cities Are Adapting to Climate Change
📊 Infographic: UN’s Climate Solutions Poster
Blog Post 6: The Paris Agreement & Climate Resilience: Global Action for a Sustainable Future
The Paris Agreement Explained
What Is It?
The Paris Agreement (2015) is a legally binding international treaty where:
- 195 countries committed to limit global warming to “well below 2°C” (ideally 1.5°C) compared to pre-industrial levels
- Nations submit NDCs (Nationally Determined Contributions) – climate action plans updated every 5 years
- Wealthy countries provide $100 billion/year to help developing nations adapt
Key Mechanisms
Mitigation: Reduce emissions through renewable energy, forest protection, etc.
Adaptation: Prepare for unavoidable impacts (sea-level rise, extreme weather)
Climate Finance: Fund clean energy + resilience projects in vulnerable countries
Progress & Challenges
Successes:
- 90% of global GDP now covered by net-zero pledges
- Renewable energy costs dropped 85% since 2010
Gaps:
- Current pledges still lead to ~2.7°C warming
- Climate finance commitments unmet
Building Climate Resilience
What Is Climate Resilience?
The capacity to:
🔹 Anticipate climate risks (e.g., flood modeling)
🔹 Adapt infrastructure/policies (e.g., drought-resistant crops)
🔹 Recover quickly from disasters
Global Case Studies
🇩🇰 Copenhagen, Denmark – Urban Flood Defense
- Challenge: Heavy rainfall flooding cities
- Solutions:
- Green roofs absorb stormwater
- Pocket parks double as water reservoirs
- Elevated streets in flood zones
- Result: Handles 30% more rainfall than conventional systems
🇧🇩 Dhaka, Bangladesh – Community Early Warnings
- Challenge: Deadly monsoon floods
- Solutions:
- Mobile alerts for 2 million residents
- Flood shelters on stilts
- Mangrove restoration to buffer storm surges
- Result: 75% fewer deaths from cyclones since 1991
🇺🇸 California, USA – Wildfire Prevention
- Challenge: Megafires from drought + heat
- Solutions:
- Controlled burns to clear dry brush
- AI fire detection cameras
- Microgrids to keep power on during outages
- Result: 2023 fires 40% smaller than 2020 peak
How These Connect
The Paris Agreement funds resilience projects like those above through:
- Green Climate Fund: $10 billion for adaptation
- Loss & Damage Fund (established 2023): Compensates climate disasters
What You Can Do
Advocate: Push leaders to strengthen NDCs
Innovate: Study climate-resilient engineering/design
Patronize climate-friendly organizations, businesses
📹 Watch: UN’s Paris Agreement Explained
📺 Watch This: BBC: How Bangladesh Is Beating Floods
📊 Infographic: 100 Resilient Cities Strategies